ridl is an R client for the UNHCR Raw Internal Data Library (RIDL) platform.
Introduction
The UNHCR RIDL platform is UNHCR internal platform to easily store, find and analyze raw data.
RIDL concepts
In order to easily use the ridl package, it’s important to understand some key concepts of this platform. RIDL documentation is available here for more details.
Container
A container is a placeholder where we can share data on RIDL. A container is represented in the ridl package as a RIDLContainer object and can hold zero or multiple datasets.
Most functions are prefixed by ridl_container or rc
- Get metadata of a container:
ridl_container_showorrc_show - Get the list of the names of all containers in the server:
ridl_container_listorrc_list
Dataset
A dataset is a placeholder where we can share data files (resources). In a dataset page there’s some metadata that give you enough context and information to properly store the data files and use them. A data file e.g an Excel file is called a resource and many of them can be shared in dataset page. In the ridl package, a RIDLDataset object is used to represent a dataset.
Most functions are prefixed by ridl_dataset or rd:
- Get metadata of a dataset and its resources:
ridl_dataset_showorrd_show - Get the list of the names of all datasets in the server:
ridl_dataset_listorrd_list - Check whether a dataset exists or not:
ridl_dataset_existorrd_exist - Searches for datasets satisfying a given search criteria:
ridl_datasets_searchorrd_search - Get the
Containerobject in which you have the dataset:ridl_datasets_container_getorrd_container_get
Resource
A resource is a file shared in dataset page, it includes microdata and supporting documents like reports or survey forms. A RIDLResource class is used to implement all the logic needed to manipulate RIDL resource.
Most functions are prefixed by ridl_resource or rr
- Get metadata of a resource:
ridl_resource_showorrr_show
Installation
This package is not on yet on CRAN and to install it, you will need the remotes package. You can get ridl from Gitlab or Github (mirror)
## install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_gitlab("dickoa/ridl")ridl: A quick tutorial
The ridl package requires you to add your API token and store it for further use. It is preferred option, you no longer need to use the API key. In order to have an API token, you need to generate one, by going to the following this URL: “ridl-server-url/user/@your-user-name/api-tokens”.
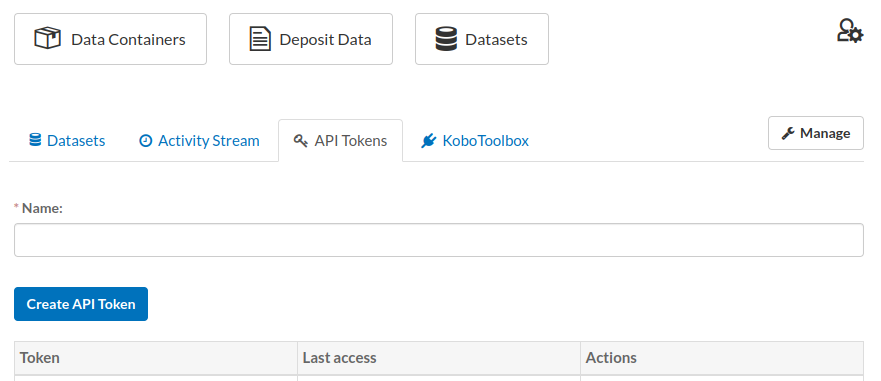
api_key_img
You give it a name, and generate a token. Once generated, you can store it in your .Renviron file which is automatically read by R on startup.
You can either edit directly the .Renviron file or access it by calling usethis::edit_r_environ() (assuming you have the usethis package installed) and entering:
RIDL_API_TOKEN=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxOnce the environment variable is set you will need to restart your session.
library("ridl")
ridl_config_get()
## <RIDL Configuration>
## RIDL site url: https://ridl.unhcr.org
## RIDL API token: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxIf you plan to use RIDL testing environment (https://ridl-uat.unhcr.org), you’ll need to also setup the RIDL_UAT_API_TOKEN variable.
RIDL_UAT_API_TOKEN=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxYou can also configure directly the ridl package using the ridl_config_setup function and check the config using ridl_config_get but it’s not persistent if you close your session.
ridl_config_setup(site = "test",
token = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx")
ridl_config_get()
## <RIDL Configuration>
## RIDL site: https://ridl-uat.unhcr.org/
## RIDL API token: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxNow that we are connected to RIDL, we can search for dataset using ridl_dataset_search.
ridl_config_setup(site = "prod")
ridl_dataset_search("mali", visibility = "public", rows = 2) ## search internally public dataset in RIDL, limit the results to two rows
## [[1]]
## <RIDL Dataset> 6f37029d-0ec2-4322-88ed-6447b2eebf3a
## Title: Socio-economic assessment of Malian refugees in Burkina Faso 2016
## Name: unhcr-bfa-2016-sea-1-1
## Visibility: public
## Resources (up to 5): DDI XML, DDI RDF, UNHCR_BFA_2016_SEA_household_v1_1, UNHCR_BFA_2016_SEA_individual_v1_1, UNHCR_BFA_2016_final report
## [[2]]
## <RIDL Dataset> 59573073-aef6-42c1-a9db-efae3f95051c
## Title: Socio-economic assessment of refugees in Mauritania's Mberra camp 2017
## Name: unhcr-mrt-2017-sea-1-1
## Visibility: public
## Resources (up to 5): DDI XML, DDI RDF, UNHCR_MRT_2017_SEA_household_v1_1, UNHCR_MRT_2017_SEA_individual_v1_1, UNHCR_MRT_2017_SEA_questionnaire
## attr(,"class")
## [1] "ridl_datasets_list"We can select a particular dataset from the list (a ridl_dataset_list is a list) of dataset using R function to access elements from list (e.g [[). In this example, we can use either purrr::pluck or dplyr::nth since they both play well with the pipe operator %>%. Once the dataset selected, it’s possible to list all its resource objects using ridl_resource_list.
library(tidyverse)
ridl_dataset_search("mali", visibility = "public", rows = 2) |>
nth(1) |>
ridl_resource_list(format = "stata")
## <RIDL Resource> 026f9547-d7b2-4ec3-bbaa-5096837b1f01
## Name: UNHCR_BFA_2016_SEA_household_v1_1
## Description: BFA SEA household level data
## Type: microdata
## Size: 1278720
## Format: Stata
## [[2]]
## <RIDL Resource> 30ab9f7a-9b84-4695-88ba-7504a4aed9e2
## Name: UNHCR_BFA_2016_SEA_individual_v1_1
## Description: BFA SEA individual data
## Type: microdata
## Size: 143744
## Format: Stata
## attr(,"class")
## [1] "ridl_resource_list"A ridl_resource_list is a simple R list and can be manipulated using purrr::pluck or dplyr::nth to select the one you want to read into your R session or download.
library(tidyverse)
ridl_dataset_search("mali", visibility = "public", rows = 2) |>
nth(1) |>
ridl_dataset_resource_get_all(format = "stata") |>
nth(1) |>
ridl_resource_read()
## + # A tibble: 1,690 x 459
## hhid q002a q006 q008 q102 q113 q200 q201
## <dbl> <dbl+l> <dbl+l> <dbl+l> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl+l> <dbl+l>
## 1 10004 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 3 0 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 2 10008 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 3 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 3 10012 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 7 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 4 10016 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 2 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 5 10020 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 6 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 6 10024 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 3 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 7 10028 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 5 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 8 10032 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 7 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 9 10036 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 4 3 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## 10 10040 1 [Cam… 1 [Oui] 1 [Pré… 2 1 2 [Dou… 1 [For…
## # … with 1,680 more rows, and 451 more variables:
## # q202 <dbl+lbl>, q203 <dbl>, q204 <dbl+lbl>, q205 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q206_1 <dbl+lbl>, q206_2 <dbl+lbl>, q206_3 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q206_4 <dbl+lbl>, q206_5 <dbl+lbl>, q206_6 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q207 <dbl+lbl>, q208 <dbl+lbl>, q209 <dbl+lbl>, q210 <dbl>,
## # q211 <dbl+lbl>, q21201 <dbl+lbl>, q21202 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q21203 <dbl+lbl>, q213 <dbl+lbl>, q214 <dbl>,
## # q215 <dbl+lbl>, q216 <dbl>, q217 <dbl+lbl>, q218 <dbl>,
## # q219 <dbl+lbl>, q220 <dbl+lbl>, q221 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q222 <dbl+lbl>, q223 <dbl+lbl>, q224 <dbl+lbl>, q225 <dbl>,
## # q226 <dbl+lbl>, q227 <dbl>, q22801 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q22802 <dbl+lbl>, q22803 <dbl+lbl>, q22804 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q22805 <dbl+lbl>, q22806 <dbl+lbl>, q22807 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q22808 <dbl+lbl>, q22809 <dbl+lbl>, q22810 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q22811 <dbl+lbl>, q229 <dbl+lbl>, q230 <dbl>,
## # q231 <dbl+lbl>, q232 <dbl>, q23301 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23302 <dbl+lbl>, q23303 <dbl+lbl>, q23304 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23305 <dbl+lbl>, q23306 <dbl+lbl>, q23307 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23308 <dbl+lbl>, q23309 <dbl+lbl>, q23310 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23311 <dbl+lbl>, q234 <dbl+lbl>, q23501 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23502 <dbl+lbl>, q23503 <dbl+lbl>, q23504 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23505 <dbl+lbl>, q23506 <dbl+lbl>, q23507 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23508 <dbl+lbl>, q23509 <dbl+lbl>, q23510 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23511 <dbl+lbl>, q23512 <dbl+lbl>, q23513 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23514 <dbl+lbl>, q23515 <dbl+lbl>, q23516 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23517 <dbl+lbl>, q23518 <dbl+lbl>, q23601 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23602 <dbl+lbl>, q23603 <dbl+lbl>, q23604 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23605 <dbl+lbl>, q23606 <dbl+lbl>, q23607 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23608 <dbl+lbl>, q23609 <dbl+lbl>, q23610 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23611 <dbl+lbl>, q23612 <dbl+lbl>, q23613 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23614 <dbl+lbl>, q237 <dbl+lbl>, q238 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23901 <dbl+lbl>, q23902 <dbl+lbl>, q23903 <dbl+lbl>,
## # q23904 <dbl+lbl>, q23909 <dbl+lbl>, q240 <dbl+lbl>, …read will not work with all resources in RIDL, so far the following format are supported: csv, xlsx, xls, dta (Stata).
I will consider adding more data types in the future, feel free to file an issue if it doesn’t work as expected or you want to add a support for a new format.
For Excel files (xlsx and xls), you can also use get_sheets to list available sheets and use the sheet paramater in read to specify the sheet you want to read (default is to read the first sheet).
Reading dataset directly
We can also use ridl_dataset_show to directly read and access a dataset object.
dataset_name <- "official-cross-border-figures-of-venezuelan-individuals"
rd_show(dataset_name) |>
rd_resource_get_all() |>
nth(1) |>
rr_read()
## + Reading sheet: VEN_Official Borders Figures
## # A tibble: 1,314 x 5
## Country `Mov Type` `Border Point` Month_Year Total_individua…
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… January-20 0
## 2 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… February-… 1
## 3 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… March-20 0
## 4 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… April-20 0
## 5 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… May-20 0
## 6 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… June-20 2
## 7 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… July-20 2
## 8 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… August-20 2
## 9 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… September… NA
## 10 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… January-20 0
# … with 1,304 more rowsIf you know the id of a RIDL Resource object you can also use directly ridl_resource_show to access directly the desired resource.
rd_show(dataset_name) |>
rd_resource_get_all() |>
nth(1)
## + <RIDL Resource> 68e39d44-88ae-49f9-b492-3635341c92be
## Name: VEN_OfficialFiguresBorders
## Description: Compilation of official figures on Venezuelan population per month per entry-exit point.
## Type: microdata
## Size: 39998
## Format: XLSX
ridl_resource_show("68e39d44-88ae-49f9-b492-3635341c92be") |>
ridl_resource_read()
## + Reading sheet: VEN_Official Borders Figures
## # A tibble: 1,314 x 5
## Country `Mov Type` `Border Point` Month_Year Total_individua…
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… January-20 0
## 2 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… February-… 1
## 3 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… March-20 0
## 4 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… April-20 0
## 5 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… May-20 0
## 6 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… June-20 2
## 7 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… July-20 2
## 8 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… August-20 2
## 9 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… September… NA
## 10 Ecuador Entry from… Aeropuerto In… January-20 0
# … with 1,304 more rowsSome other handy functions
ct <- ridl_container_list(sort = "package_count")
head(ct)
## [1] "ethiopia-sens" "data-deposit" "kenya-sens"
## [4] "afghanistan" "bangladesh-sens" "south-sudan-sens"
grep("niger-", ct, ignore.case = TRUE, value = TRUE)
## [1] "niger-protection" "niger-sens"
ridl_container_show("niger-protection")
## <RIDL Container> d341942e-547e-404b-bcdf-c72b2cd85530
## Name: niger-protection
## Display name: Niger: Protection
## No. Datasets: 5
## No. Members: 3
ridl_container_show("niger-protection") |>
ridl_dataset_list()
## [1] "enrolement-pdi-tillaberi-tillaberi-niger-2020"
## [2] "identify-asylum-seekers-in-migration-flow-agadez-niger-2018-2019-2020"
## [3] "monitoring-the-migration-flow-1-agadez-niger-2019-2020"
## [4] "enrolement-pdi-tahoua-aout-2020-tahoua-niger-2020"
## [5] "enrolement-pdi-maradi-maradi-niger-2020"Create a dataset
It’s possible to create a RIDLDataset object we can manipulate and upload to the RIDL platform.
ridl_dataset(name = "test-dataset-pen",
title = "Test Dataset PEN",
notes = "Some description",
owner_org = "africa",
data_collector = "unhcr",
keywords = list(3, 4),
unit_of_measurement = "kg",
data_collection_technique = "f2f",
archived = FALSE,
visibility = "restricted",
external_access_level = "data_enclave")
## <RIDL Dataset>
## Title: Test Dataset PEN
## Name: test-dataset-pen
## Visibility: restricted
## Container: Africa
## Resources (up to 5):
ds <- ridl_dataset(name = "test-dataset",
title = "Test Dataset",
notes = "An example dataset",
owner_org = "west-africa",
data_collector = "ACF, UNHCR",
keywords = list(3, 4),
unit_of_measurement = "individual",
data_collection_technique = "f2f",
sampling_procedure = "nonprobability",
operational_purpose_of_data = "cartography",
archived = "False",
visibility = "restricted",
external_access_level = "open_access")
ds
## <RIDL Dataset>
## Title: Test Dataset
## Name: test-dataset
## Visibility: public
## Resources (up to 5):ridl_resource can also be used to create a RIDLResource.
rs <- ridl_resource(name = "Test resource",
type = "data",
format = "CSV",
file_type = "microdata",
identifiability = "anonymized_public",
date_range_start = "2018-01-01",
date_range_end = "2019-01-01",
process_status = "anonymized",
visibility = "public",
version = 1L)
rs
## <RIDL Resource>
## Name: Test resource
## Description:
## Type: microdata
## Size:
## Format: CSVWe can add the resource to the dataset and upload it to the RIDL platform.
ds |>
ridl_dataset_resource_add(rs)
ds
## <RIDL Dataset>
## Title: Test Dataset
## Name: test-dataset
## Visibility: restricted
## Resources (up to 5): Test resourceMeta
- Please report any issues or bugs.
- License: MIT
- Please note that this project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By participating in this project you agree to abide by its terms.

